Introduction
In the age of data-driven marketing, businesses are constantly seeking ways to understand their customers better. But with growing concerns around privacy, consent, and data misuse, traditional data collection methods—like third-party cookies and behavioral tracking—are losing favor. Enter zero-party data, a concept that’s reshaping how brands build trust and deliver personalized experiences. Let’s see Zero-Party Data: Building Trust Through Voluntary User Insights Relationship Based Marketing.
Zero-party data is not just a buzzword; it’s a strategic shift toward transparency, user empowerment, and ethical marketing. This blog explores what zero-party data is, why it matters, how to collect it, and how it can be used to create meaningful, trust-based relationships with customers.
What Is Zero-Party Data – Relationship Based Marketing?
Coined by Forrester Research, zero-party data refers to data that a customer intentionally and proactively shares with a brand. Unlike first-party data (collected through user behavior) or third-party data (gathered from external sources), zero-party data is voluntarily provided by users.
Examples of Zero-Party Data:
- Preferences and interests
- Purchase intentions
- Personal goals
- Feedback and survey responses
- Customization choices
Why Zero-Party Data Matters in 2025
1. Privacy Regulations
With laws like GDPR, CCPA, and India’s DPDP Act, businesses must prioritize consent and transparency. Zero-party data is inherently compliant.
2. Cookie Deprecation
Browsers like Chrome are phasing out third-party cookies. Zero-party data offers a future-proof alternative.
3. Consumer Trust
Users are more likely to engage with brands that respect their privacy and ask for input rather than track them covertly.
4. Better Personalization
Because it’s explicitly provided, zero-party data leads to more accurate and relevant personalization.
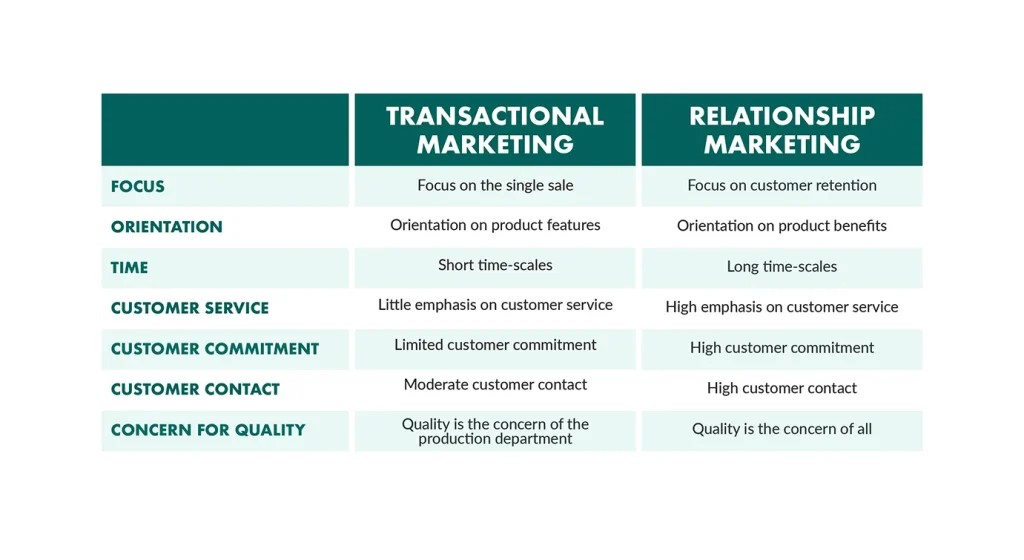
Zero-Party vs First-Party vs Third-Party Data
| Type | Source | Consent | Accuracy | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Party | User-provided | Explicit | High | Personalization, segmentation |
| First-Party | User behavior | Implicit | Medium | Analytics, retargeting |
| Third-Party | External sources | Often unclear | Variable | Broad targeting, enrichment |
How to Collect Zero-Party Data – Relationship Based Marketing
✅ Interactive Quizzes
Ask users about their preferences, needs, or style. Example: “What’s your skincare type?”
✅ Preference Centers
Let users choose what content or products they want to see.
✅ Surveys and Polls
Gather feedback on products, services, or experiences.
✅ Onboarding Forms
Use sign-up flows to ask about goals, interests, or usage patterns.
✅ Conversational Interfaces
Chatbots and virtual assistants can collect data through natural dialogue.
✅ Gamified Experiences
Use rewards and progress tracking to encourage voluntary data sharing.
Best Practices for Zero-Party Data Collection
1. Be Transparent
Tell users why you’re asking for data and how it will be used.
2. Offer Value
Provide personalized recommendations, exclusive offers, or better service in exchange.
3. Keep It Simple
Avoid long forms. Use progressive profiling to collect data over time.
4. Respect Consent
Allow users to opt out or update their preferences easily.
5. Ensure Security
Protect user data with encryption and secure storage.
Using Zero-Party Data for Personalization
🎯 Product Recommendations
Tailor suggestions based on user-stated preferences.
📧 Email Marketing
Send relevant content based on interests and goals.
🛍️ E-Commerce Experiences
Customize homepage, filters, and promotions.
📱 App Interfaces
Adapt UI and features based on user needs.
🧠 Content Strategy
Create blogs, videos, and guides that match user interests.
Real-World Examples
🧴 Sephora
Uses quizzes to recommend beauty products based on skin type and goals.
🛒 Stitch Fix
Collects style preferences to curate personalized clothing boxes.
🧘 Headspace
Asks users about stress levels and goals to tailor meditation sessions.
🏥 Mayo Clinic
Uses symptom checkers and health goals to personalize content and care pathways.
Challenges in Zero-Party Data Strategy
⚠️ User Fatigue
Too many questions can overwhelm users. Balance is key.
⚠️ Data Silos
Collected data must be integrated across systems for effective use.
⚠️ Misuse Risk
Using data in ways users didn’t expect can erode trust.
⚠️ Scalability
Collecting and managing zero-party data at scale requires robust infrastructure.
Tools and Platforms for Zero-Party Data
- Typeform / Jotform – Interactive forms and surveys
- Segment / Tealium – Customer data platforms
- Klaviyo / Mailchimp – Email personalization
- Qualtrics / SurveyMonkey – Feedback collection
- HubSpot / Salesforce – CRM integration

Zero-Party Data in the Context of AI and Automation
AI can enhance zero-party data usage by:
- Predicting user needs based on stated preferences
- Automating personalized content delivery
- Detecting changes in user behavior and prompting updates
However, AI must be used ethically, ensuring transparency and user control.
Future Trends in Zero-Party Data
1. Privacy-First UX Design
Interfaces will be built to encourage voluntary data sharing through trust and clarity.
2. Decentralized Data Ownership
Users may store and control their data via blockchain or personal data vaults.
3. Real-Time Personalization
Zero-party data will power dynamic experiences that adapt instantly.
4. Voice and Gesture-Based Data Collection
Smart assistants and wearables will gather preferences through natural interaction.
Conclusion
Zero-party data represents a shift from surveillance-based marketing to relationship-based marketing. By inviting users to share insights voluntarily, brands can build trust, deliver better experiences, and future-proof their strategies in a privacy-conscious world. In 2025 and beyond, the most successful businesses will be those that treat data not as a commodity—but as a conversation.





