Introduction
Mobile apps have become essential tools for businesses, startups, and creators to engage users, streamline operations, and generate revenue. But building a successful app isn’t just about writing code—it’s a strategic Mobile App Development Process that involves planning, design, development, testing, and ongoing optimization.
Whether you’re a business owner looking to launch an app or a designer collaborating with developers, understanding the mobile app development process can help you make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes.
This guide walks you through each stage of mobile app development—from idea to launch and beyond.
1. Ideation and Goal Setting
What Happens Here:
- Define the app’s purpose
- Identify target users
- Set clear business goals
- Analyze competitors
- Brainstorm core features
Why It Matters:
A strong foundation ensures your app solves real problems and aligns with user needs. This phase helps avoid feature bloat and keeps development focused.
Deliverables:
- App concept document
- User personas
- Feature list
- Success metrics
2. Market Research and Validation
What Happens Here:
- Study market trends
- Analyze competitors’ apps
- Conduct surveys or interviews
- Validate demand and usability
Why It Matters:
Market research helps you understand what users expect and what gaps exist. Validation ensures you’re not building something nobody wants.
Deliverables:
- SWOT analysis
- Competitive feature comparison
- User feedback summary
3. Choosing the Right Technology Stack
Options:
- Native Development: Swift (iOS), Kotlin (Android)
- Cross-Platform: Flutter, React Native
- Hybrid Apps: Ionic, Cordova
- Backend: Node.js, Firebase, Django
Factors to Consider:
- Budget
- Timeline
- Performance needs
- Team expertise
Deliverables:
- Tech stack recommendation
- Architecture blueprint
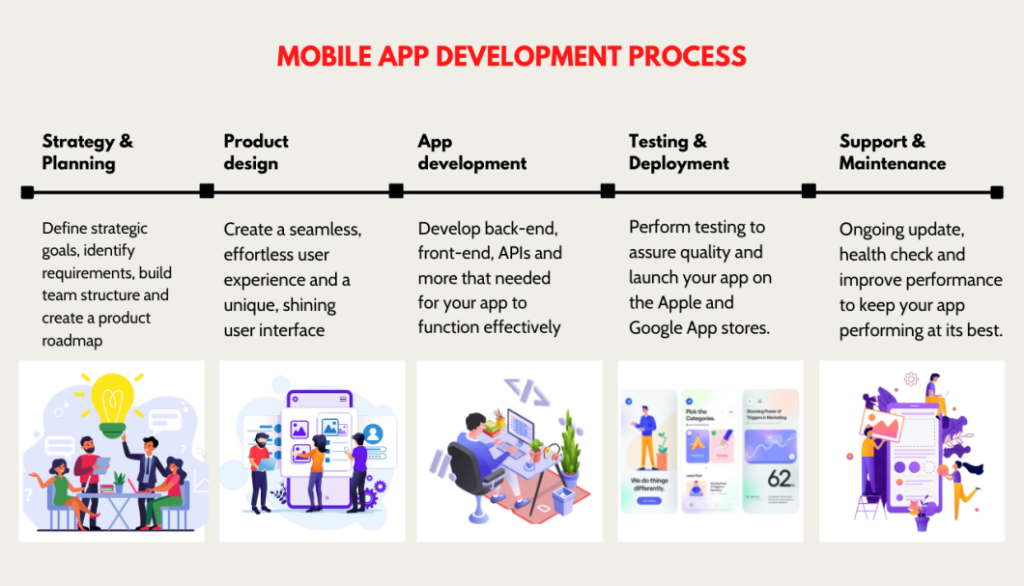
4. Wireframing and UX Design
What Happens Here:
- Sketch user flows
- Create wireframes
- Design UI mockups
- Plan navigation and interactions
Tools Used:
- Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch
Why It Matters:
Good design improves usability, retention, and conversion. Wireframes help visualize the app before development begins.
Deliverables:
- Wireframes
- UI mockups
- User journey maps
5. Prototyping and User Testing
What Happens Here:
- Build interactive prototypes
- Conduct usability testing
- Gather feedback
- Refine design
Tools Used:
- InVision, Marvel, Proto.io
Why It Matters:
Testing early helps catch usability issues before development, saving time and money.
Deliverables:
- Clickable prototype
- Usability test reports
- Design revisions
6. Front-End Development
What Happens Here:
- Code the app’s interface
- Implement animations and transitions
- Ensure responsiveness across devices
Languages Used:
- Swift, Kotlin, Dart, JavaScript
Why It Matters:
Front-end development brings the design to life and ensures users have a smooth experience.
Deliverables:
- Functional UI screens
- Integrated design elements
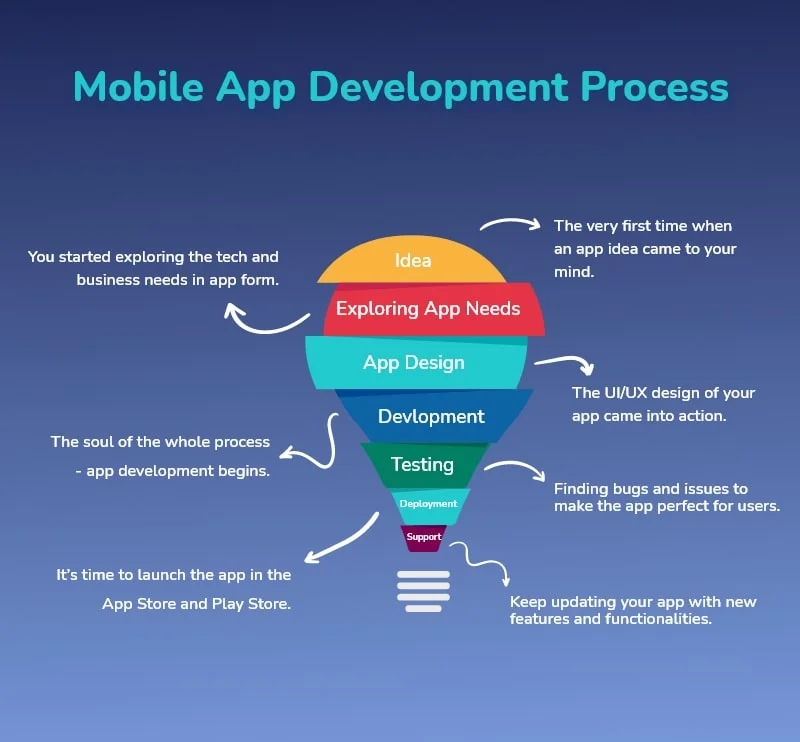
7. Back-End Development
What Happens Here:
- Set up servers and databases
- Build APIs
- Handle user authentication
- Manage data storage and retrieval
Languages Used:
- Node.js, Python, PHP, Java
Why It Matters:
The back-end powers the app’s logic, data, and security. It’s the engine behind the interface.
Deliverables:
- API documentation
- Database schema
- Server-side code
8. Integration and Feature Development
What Happens Here:
- Connect front-end to back-end
- Add core features (e.g., login, payments, notifications)
- Integrate third-party services (e.g., Google Maps, Stripe)
Why It Matters:
This phase turns your app into a fully functional product with real-world capabilities.
Deliverables:
- Working app features
- Integrated services
- Feature testing reports
9. Testing and Quality Assurance
Types of Testing:
- Functional testing
- Usability testing
- Performance testing
- Security testing
- Device compatibility testing
Tools Used:
- Appium, TestFlight, Firebase Test Lab
Why It Matters:
Testing ensures your app works as intended, is secure, and performs well across devices.
Deliverables:
- Bug reports
- Test case documentation
- QA sign-off
10. Deployment and Launch
What Happens Here:
- Prepare app store listings
- Submit to Apple App Store and Google Play
- Handle approvals and rejections
- Monitor launch performance
Why It Matters:
A smooth launch sets the tone for user adoption and reviews. App store optimization (ASO) helps improve visibility.
Deliverables:
- App store assets (screenshots, descriptions)
- Live app on stores
- Launch analytics dashboard

11. Post-Launch Support and Maintenance
What Happens Here:
- Monitor crashes and bugs
- Release updates and patches
- Add new features based on feedback
- Optimize performance
Why It Matters:
Apps are living products. Continuous improvement keeps users engaged and loyal.
Deliverables:
- Maintenance plan
- Update roadmap
- User feedback reports
12. Marketing and Growth Strategy
What Happens Here:
- Promote app via social media, ads, influencers
- Use push notifications and email campaigns
- Analyze user behavior and retention
Tools Used:
- Mixpanel, Google Analytics, Firebase
Why It Matters:
Marketing drives downloads, while analytics helps refine your strategy.
Deliverables:
- Marketing assets
- Growth KPIs
- Retention strategy
13. Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes That Cost Time and Money:
- Skipping user research
- Overloading features in MVP
- Ignoring testing
- Poor communication between teams
- Underestimating post-launch needs
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures smoother development and better ROI.
Conclusion
Mobile app development is a multi-stage journey that requires collaboration, planning, and adaptability. By following a structured process—from ideation to post-launch—you can build an app that not only works but delights users and drives business growth.
Whether you’re building a simple utility app or a complex platform, understanding each step helps you stay in control, make informed decisions, and deliver a product that stands out in the crowded app marketplace.





