Introduction
WordPress Performance is a critical factor in user experience, SEO rankings, and conversion rates. A slow-loading WordPress site can frustrate visitors, increase bounce rates, and hurt your visibility in search engines. Fortunately, two powerful techniques—caching and minification—can dramatically improve your site’s speed and responsiveness.
In this blog, we’ll explore how caching and minification work, why they matter, and how to implement them effectively in WordPress. Whether you’re a developer, designer, or site owner, these strategies will help you deliver a faster, smoother experience to your users.
1. Why WordPress Performance Matters
User Experience
- Faster sites reduce bounce rates and increase engagement.
- Users expect pages to load in under 2 seconds.
SEO
- Google uses page speed as a ranking factor.
- Core Web Vitals emphasize performance metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and First Input Delay (FID).
Conversions
- A 1-second delay can reduce conversions by up to 7%.
- Faster checkout and navigation lead to higher sales and sign-ups.
2. What Is Caching?
Caching stores copies of your website’s content so it can be delivered faster to users.
Types of Caching
- Browser Caching: Stores static files (images, CSS, JS) in the user’s browser.
- Page Caching: Saves full HTML pages to reduce server processing.
- Object Caching: Stores database query results to speed up dynamic content.
- Opcode Caching: Caches compiled PHP code to reduce server load.
How It Works
Instead of generating a page from scratch every time, caching serves a saved version—reducing server load and speeding up delivery.
3. What Is Minification?
Minification removes unnecessary characters from code (spaces, comments, line breaks) to reduce file size.
Files Commonly Minified
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
Benefits
- Smaller files load faster
- Reduces bandwidth usage
- Improves rendering speed
Minification doesn’t change functionality—it simply makes code leaner.
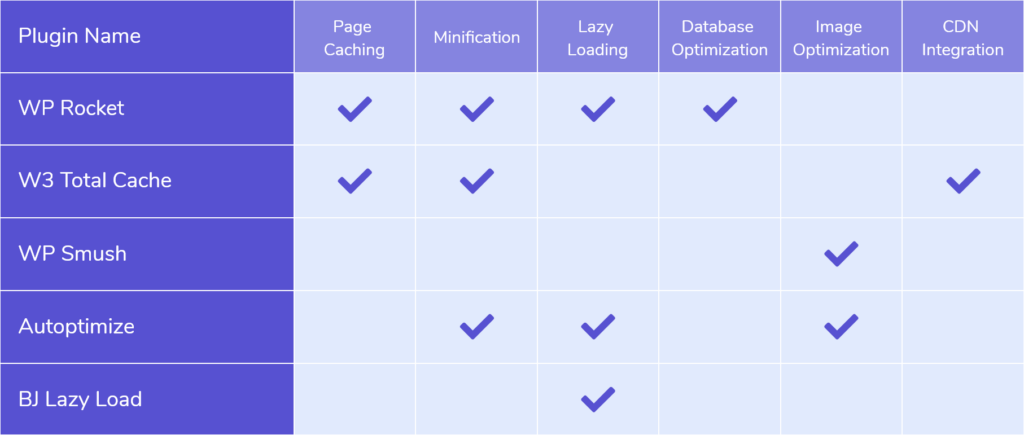
4. Tools and Plugins for Caching in WordPress
1. WP Rocket
- Premium plugin with page caching, browser caching, and database optimization.
- User-friendly interface and automatic setup.
2. W3 Total Cache
- Free and powerful with support for page, object, and browser caching.
- Advanced settings for developers.
3. LiteSpeed Cache
- Works best with LiteSpeed servers.
- Includes image optimization and CDN integration.
4. Cache Enabler
- Lightweight and simple.
- Ideal for small sites or beginners.
5. SiteGround Optimizer
- Built for SiteGround-hosted sites.
- Includes dynamic caching and front-end optimization.
5. Tools and Plugins for Minification in WordPress
1. Autoptimize
- Minifies HTML, CSS, and JS.
- Combines files and supports CDN integration.
2. WP Rocket
- Includes minification and file combination.
- Easy to enable with one click.
3. Fast Velocity Minify
- Advanced control over file handling.
- Ideal for developers needing granular settings.
4. Asset CleanUp
- Minifies and unloads unused CSS/JS files.
- Helps reduce bloat from plugins.
6. How to Implement Caching in WordPress
Step-by-Step Guide
- Choose a caching plugin based on your hosting and site needs.
- Install and activate the plugin.
- Enable page caching to store full HTML pages.
- Enable browser caching to store static assets.
- Configure object caching if your site uses dynamic content.
- Test performance using tools like GTmetrix or PageSpeed Insights.
Tips
- Clear cache after updates or design changes.
- Use cache preloading to improve first-time visits.
- Avoid caching admin pages or user-specific content.
7. How to Implement Minification in WordPress
Step-by-Step Guide
- Install a minification plugin like Autoptimize or WP Rocket.
- Enable HTML, CSS, and JS minification in settings.
- Combine files to reduce HTTP requests.
- Exclude problematic files if minification breaks functionality.
- Test site performance and layout after enabling minification.
Tips
- Use staging environments to test changes.
- Monitor for broken layouts or scripts.
- Combine minification with CDN for best results.
8. Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Caching Issues
- Stale content: Clear cache regularly or use cache expiration.
- Plugin conflicts: Test compatibility before activating.
- Dynamic content: Use cache exclusions for user-specific pages.
Minification Issues
- Broken layouts: Exclude critical CSS files.
- JavaScript errors: Avoid combining incompatible scripts.
- Plugin conflicts: Use selective minification.
Always test changes thoroughly and monitor performance metrics.
9. Advanced Optimization Techniques
1. CDN Integration
- Distribute content globally for faster delivery.
- Popular CDNs: Cloudflare, BunnyCDN, StackPath
2. Image Optimization
- Compress images without quality loss.
- Use plugins like ShortPixel or Smush.
3. Lazy Loading
- Load images and videos only when needed.
- Reduces initial page load time.
4. Database Optimization
- Clean up post revisions, spam comments, and transients.
- Use WP-Optimize or Advanced Database Cleaner.
5. GZIP Compression
- Compress files before sending to browsers.
- Enabled via server or plugin settings.

10. Measuring Performance Improvements
Use these tools to track your optimization efforts:
1. Google PageSpeed Insights
- Measures Core Web Vitals
- Offers suggestions for improvement
2. GTmetrix
- Detailed waterfall analysis
- Grades performance and structure
3. Pingdom Tools
- Tests from multiple locations
- Tracks load time and file sizes
4. WebPageTest
- Advanced testing with filmstrip view
- Simulates real-world conditions
Compare before-and-after results to quantify impact.
11. Case Study: Speed Optimization for a WordPress Blog
Site: Lifestyle blog with 100+ posts and heavy image use
Challenge: Slow load times and high bounce rate
Actions Taken:
- Installed WP Rocket for caching and minification
- Enabled lazy loading and image compression
- Integrated Cloudflare CDN
- Cleaned up database and reduced plugin bloat
Results:
- Page load time reduced from 4.2s to 1.3s
- Bounce rate dropped by 22%
- Organic traffic increased by 18% in 3 months
This shows how simple optimizations can yield big results.
Conclusion
Caching and minification are two of the most effective ways to boost WordPress performance. They reduce server load, speed up page delivery, and enhance user experience—all while improving SEO and conversions.
Whether you’re running a blog, e-commerce store, or portfolio site, these techniques are essential for staying competitive in today’s fast-paced digital landscape. Start with the right tools, test thoroughly, and monitor your results. Your users—and your bottom line—will thank you.





