Introduction
In the crowded digital landscape, grabbing attention and driving action through ads is more challenging than ever. Behavioral Psychology to Improve Ad powerful toolkit for marketers and designers to understand how people think, feel, and act—allowing for more persuasive and effective advertising. This blog explores how principles from behavioral psychology can be applied to improve ad performance, from design and copywriting to targeting and timing.
1. What Is Behavioral Psychology in Advertising?
Behavioral psychology studies how people make decisions and what influences their behavior. In advertising, it helps decode:
- Cognitive biases (e.g., anchoring, loss aversion)
- Emotional triggers (e.g., fear, joy, urgency)
- Decision-making processes (e.g., heuristics, framing)
Understanding these elements allows advertisers to craft messages that resonate deeply and drive conversions.
2. The Power of Cognitive Biases in Ads
Anchoring Effect
People rely heavily on the first piece of information they see. Use this by:
- Showing a higher “original price” before the discounted one
- Presenting premium options first to make others seem more affordable
Loss Aversion
Consumers fear losing more than they enjoy gaining. Tactics include:
- “Limited-time offer” or “Only 3 left in stock”
- Highlighting what users miss out on by not acting
Social Proof
People follow the crowd. Boost trust and conversions with:
- Testimonials and reviews
- “X people bought this today” notifications
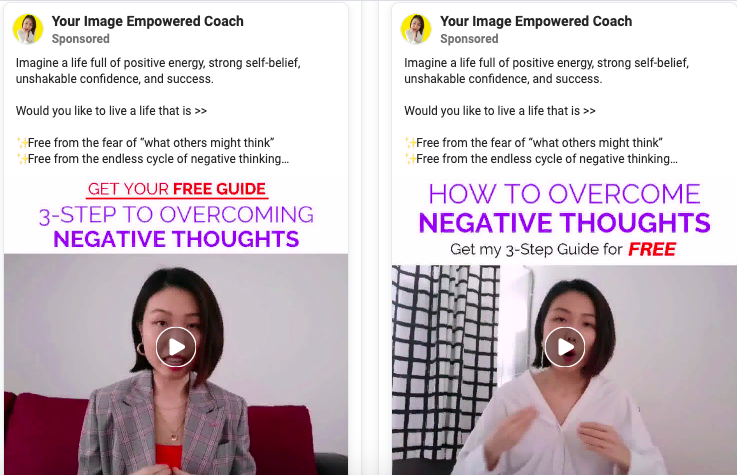
3. Emotional Triggers That Drive Action
Fear and Urgency
Fear-based messaging can prompt quick decisions, especially when paired with urgency:
- “Don’t miss out!”
- “Protect your data before it’s too late”
Joy and Aspiration
Positive emotions build brand affinity:
- Use aspirational imagery and language
- Showcase benefits that improve lifestyle or status
Trust and Safety
Especially important in finance, health, and tech:
- Use secure symbols (padlocks, HTTPS)
- Include guarantees and return policies
4. The Role of Framing and Priming
Framing
How information is presented affects perception:
- “95% fat-free” vs. “5% fat”
- “Save ₹500” vs. “Avoid spending ₹500”
Priming
Subtle cues influence behavior:
- Use color psychology (e.g., red for urgency, blue for trust)
- Preload users with positive associations before a CTA
5. Personalization and Behavioral Targeting
Behavioral psychology thrives on relevance. Use data to:
- Serve ads based on browsing history or past purchases
- Customize messaging to user personas (e.g., value-seekers vs. luxury buyers)
Tools like retargeting and dynamic creative optimization make this scalable.
6. The Psychology of Ad Design
Visual Hierarchy
Guide the eye using:
- Size, contrast, and placement
- Clear CTA buttons with action-oriented text
Color Psychology
Colors evoke emotions:
- Red: urgency, excitement
- Blue: trust, calm
- Green: growth, eco-friendliness
Typography
Fonts influence tone:
- Serif fonts: tradition, reliability
- Sans-serif fonts: modernity, clarity
7. Copywriting That Converts
Use of Power Words
Words like “free,” “exclusive,” “guaranteed,” and “instantly” trigger emotional responses.
Storytelling
Narratives create emotional engagement:
- Share customer success stories
- Use relatable scenarios to build empathy
Clarity and Simplicity
Avoid jargon. Make the message easy to understand and act on.

8. Behavioral Psychology in Different Ad Formats
Display Ads
- Use bold visuals and concise messaging
- Leverage urgency and social proof
Video Ads
- Tell a story quickly
- Use emotional music and visuals
Search Ads
- Focus on relevance and clarity
- Use keywords that match user intent
9. Testing and Optimization
Behavioral psychology isn’t one-size-fits-all. Use:
- A/B testing to compare psychological triggers
- Heatmaps to analyze attention patterns
- Conversion tracking to measure effectiveness
10. Ethical Considerations
While behavioral psychology can be powerful, it must be used responsibly:
- Avoid manipulation or fear-mongering
- Be transparent about data usage
- Respect user autonomy and consent
Conclusion
Behavioral psychology offers a rich framework for crafting ads that don’t just look good—they work. By understanding how people think and feel, advertisers can create campaigns that connect, persuade, and convert. Whether you’re designing a banner ad or writing a video script, integrating psychological principles can elevate your strategy and deliver measurable results.





